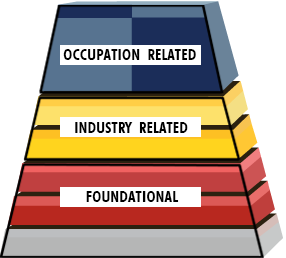
The competency models on the Competency Model Clearinghouse (CMC) are based on a tiered "building block" framework. Each building block represents a competency—a cluster of related skills, knowledge, and abilities that affect a major part of one’s job—that is essential for successful performance in the industry or occupation represented by the model. Users can revise, remove, or add new building blocks to create their own customized competency models that reflect the skills, knowledge, and abilities needed in their industry or occupation.
The building blocks are arranged in tiers of related competencies. The arrangement of the tiers in a pyramidal shape represents the increasing level of specificity and specialization of the content on the upper tiers of the pyramid. The tiers of the building block framework include:
 Click on the image to view models
Click on the image to view models
Industry Related
- Tier 5 - Industry-Sector Technical Competencies
- Tier 4 - Industry-Wide Technical Competencies
Foundational Competencies
- Tier 3 - Workplace Competencies
- Tier 2 - Academic Competencies
- Tier 1 - Personal Effectiveness Competencies
At the bottom of the model, the competencies apply to a large number of occupations and industries. As one moves up the tiers of the model, the competencies become specific to industries and occupations. The graphic is not intended to represent a sequential relationship between the tiers or to imply that all competencies on a lower tier must be achieved prior to tackling a competency on a higher-level tier. Acquisition and demonstration of the foundational competencies, coupled with attainment and performance of industry and occupation-specific knowledge, skills and abilities, are important to both individual and organizational success.
Foundational Competencies
At the base of the model, Tiers 1 through 3 represent those competencies that provide the foundation for success in school and in the world of work. Employers have identified a link between foundational skills and job performance, and foundational skills are often a prerequisite for workers to learn new industry-specific skills. These foundational competencies are essential to a large number of occupations and industries and can be found in the Building Blocks Model, which is often used as the starting point for development of other competency models.
Tier 1: Personal Effectiveness Competencies
Personal Effectiveness Competencies are shown at the base of the pyramid because these competencies are essential for all life roles—roles as a member of a family, a community, and a larger society. They are included in the model framework because these competencies, sometimes referred to as "soft skills," are also valued in the labor market. Personal effectiveness competencies are generally learned in the home or community and reinforced and honed at school and in the workplace. They represent personal attributes that may be challenging to teach or assess. Personal Effectiveness Competencies include:
- Interpersonal Skills
- Integrity
- Professionalism
- Initiative
- Dependability and Reliability
- Adaptability and Flexibility
- Lifelong Learning
Tier 2: Academic Competencies
In the second tier of the model are Academic Competencies. This tier contains critical competencies primarily learned in an academic setting, as well as cognitive functions and thinking styles. These competencies are likely to apply to all organizations in a single industry or represented by an industry association nationwide. They serve as the foundation for the Occupation and Industry Competencies. These competencies include:
- Reading
- Writing
- Mathematics
- Science and Technology
- Communication
- Critical and Analytic Thinking
- Basic Computer Skills
Tier 3: Workplace Competencies
The third tier consists of Workplace Competencies. Competencies included in this tier represent those skills and abilities that allow individuals to function in an organizational setting. As with the Academic Competencies, these are generally applicable to a large number of occupations and industries on a national level. The competencies in this tier include:
- Teamwork
- Customer Focus
- Planning and Organizing
- Creative Thinking
- Problem Solving and Decision-Making
- Working with Tools and Technology
- Scheduling and Coordinating
- Checking, Examining, and Recording
- Business Fundamentals
- Sustainable Practices
- Health and Safety
Foundational competencies are frequently referred to as Work Readiness Competencies.
Search for examples of Foundation Models
Industry Competencies
The competencies shown on Tiers 4 and 5 describe cross-cutting, industry- and sector-wide skills, knowledge, and abilities. Referred to collectively as Industry Competencies, their applicability to roles throughout the industry or sector makes it possible to identify career pathways that enable workers to move across industry sub-sectors with similar competency requirements. This supports the development of an agile workforce, rather than limiting career paths to a single occupational career ladder.
Tier 4: Industry-Wide Technical Competencies
Industry-Wide Technical Competencies are contained in the fourth tier. Competencies included in this tier represent the knowledge, skills and abilities needed by all occupations within an industry. These competencies must be determined for each industry or profession and therefore are not defined in the Building Blocks Model. Representatives of an industry or profession specify and define these competencies as part of the competency model development process.
Tier 5: Industry-Sector Technical Competencies
At the fifth level of the pyramid are the Industry-Sector Technical Competencies. Competencies included in this tier represent the knowledge, skills, abilities and other characteristics needed by all occupations within an industry sector (e.g., the Air Transportation sector of the Transportation Industry). Like the Industry-Wide Competencies, these competencies are not defined in the Building Blocks Model and are meant to be specified and defined as part of the competency model development process. These competencies can be further refined and updated to meet regional or local industry and employer needs as part of sector partnerships, using the tools and convening guides available in this CMC.
Search for Industry Model Resources
Occupation Competencies
The competencies on Tier 6 are referred to as Occupation Competencies. While the focus of the CMC is on industry competencies, some stakeholder groups seek to identify and call out specific occupational competencies to define performance in a workplace, design competency-based curricula, or articulate the requirements for an occupational credential such as a license or certification.
Tier 6 provides a place to identify those competencies, or alternatively to link to existing occupational information as defined in the Occupational Information Network (O*NET) system. Many model pyramids have a link to relevant O*NET occupations that occur in an industry in the right-hand side of the blue Tier 6 of the model. The left-hand side of the Tier 6 may be used to highlight overarching management competencies—listed below. The O*NET system provides information on over 900 occupations, including Tasks, Work Activities, Knowledge, Skills, Abilities, and other characteristics.
Tier 6 left-hand block: Management Competencies
The competencies included in the Management Competencies domain are specific to supervisory and managerial occupations and include:
- Staffing
- Informing
- Delegating
- Networking
- Monitoring Work
- Entrepreneurship
- Supporting Others
- Motivating and Inspiring
- Developing and Mentoring
- Strategic Planning/Action
- Preparing and Evaluating Budgets
- Clarifying Roles and Objectives
- Managing Conflict and Team Building
- Developing an Organizational Vision
- Monitoring and Controlling Resources
Search for Occupational Competency Model Resources